Chapter 7
Motion
Page-100
Questions-
1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
Ans-
2. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds from his initial position?
Ans-
3. Which of the following is true for displacement?
(a) It cannot be Zero.
(b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Ans-
Page- 102
Questions-
1. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Ans-
2. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average of an object equal to its average speed?
Ans-
3. What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
Ans-
4. What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
Ans-
5. During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes. What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is, 3 × 10⁸ m sー¹.
Ans-
Page-103
Questions-
1. When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration? (ii) nonuniform acceleration?
Ans-
2. A bus decreases its speed form 80 km hー¹ to 60 km hー¹ in 5 s. Find the acceleration of the bus.
Ans-
3. A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed 40 km hー¹ in 10 minutes. Find its accceleration.
Ans-
Page-107
Questions-
প্ৰশ্ন-
1. What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Ans-
2. What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graphs is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Ans-
3. What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graphs is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Ans-
4. What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
Ans-
Page-109
Questions-
1. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m sー² for 2 minutes. Find (a) the speed acquired. (b) the distance travelled.
Ans-
2. A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km hー¹. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of 0.5 m sー². Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Ans-
3. A trolley, while going down an inclined plane, has an acceleration of 2 cm sー². What will be its velocity 3 s after the start?
Ans-
4. A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 m sー². What distance will it cover in 10 s after start?
Ans-
5. A stone is thrown in a vertically upward direction with a velocity of 5 m sー¹. If the acceleration of the stone during its motion is 10 m sー² in the downward direction, what will be the height attained by the stone and how much time will it take to reach there?
Ans-
Exercises-
1. An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 minutes 20 s?
2. Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes 30 seconds and then turns around and jogs 100 m back to point C in another 1 minute. What are Joseph’s average speeds and velocities in jogging (a) from A to B and (b) from A to C?

4. A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of 3.0 m s–2 for 8.0 s. How far does the boat travel during this time?

(b) Which part of the graph represents uniform motion of the car?
6. Fig 7.10 shows the distance-time graph of three objects A, B and C. Study the graph and answer the following questions:
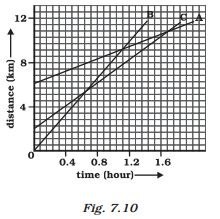
(a) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
(b) Are all three ever at the same point on the road?
(c) How far has C travelled when B passes A?
(d) How far has B travelled by the time it passes C?
7. A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m s-2, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
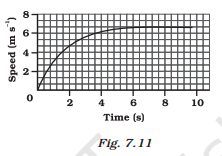
8. The speed-time graph for a car is shown is Fig. 7.11.